FPS
Framestore Preproduction Services (FPS) enables film-makers and showrunners to make early-stage, creative decisions that can then guide their entire production.
We have over a hundred creatives, technologists and producers working across concept art, previsualisation, virtual production, in-camera VFX (ICVFX), techvis and postvis.
This unique pool of world-class minds and skills allow us to serve as true creative collaborators, whether the production in question requires initial character design, logistical assistance for a single complex sequence or a ‘beginning to end’ offer that begins with concept art and culminates in our award-winning final VFX.

Concept Design
/art-department

Previsualisation
/pre-visualisation
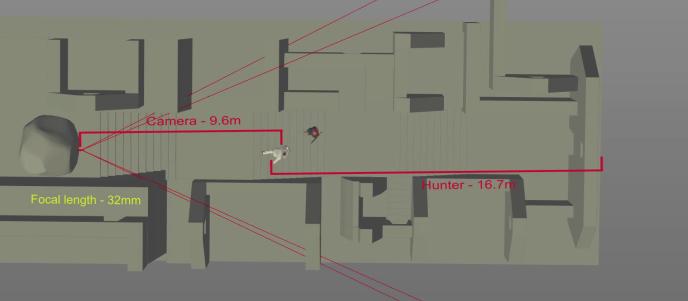
Tech-Visualisation
/tech-visualisation

Post-Visualisation
/post-visualisation

LED Volumes
/led-volumes

On Set Visualisation
/set-visualisation

Virtual Scouting
/virtual-scouting-and-camera

Performance Capture
/performance-capture

Virtual Art Department
/virtual-art-department

Visualisation Supervisors
/talent?job=Pre-Production%20Supervisor&pillar=Film&location=